By Sam Rauf, Senior Economic Development Manager, WCED
*This is part 2 of a 3-part series where we take a deeper dive into workforce trends impacting the Triangle Region. In our first post, we explored nationwide trends in the labor market and the rapidly changing environment we find ourselves in. This post explores what the national trends mean for us here in the Triangle utilizing insights from the Regional Skills Analysis. The final portion of the series will include reactions from local workforce.
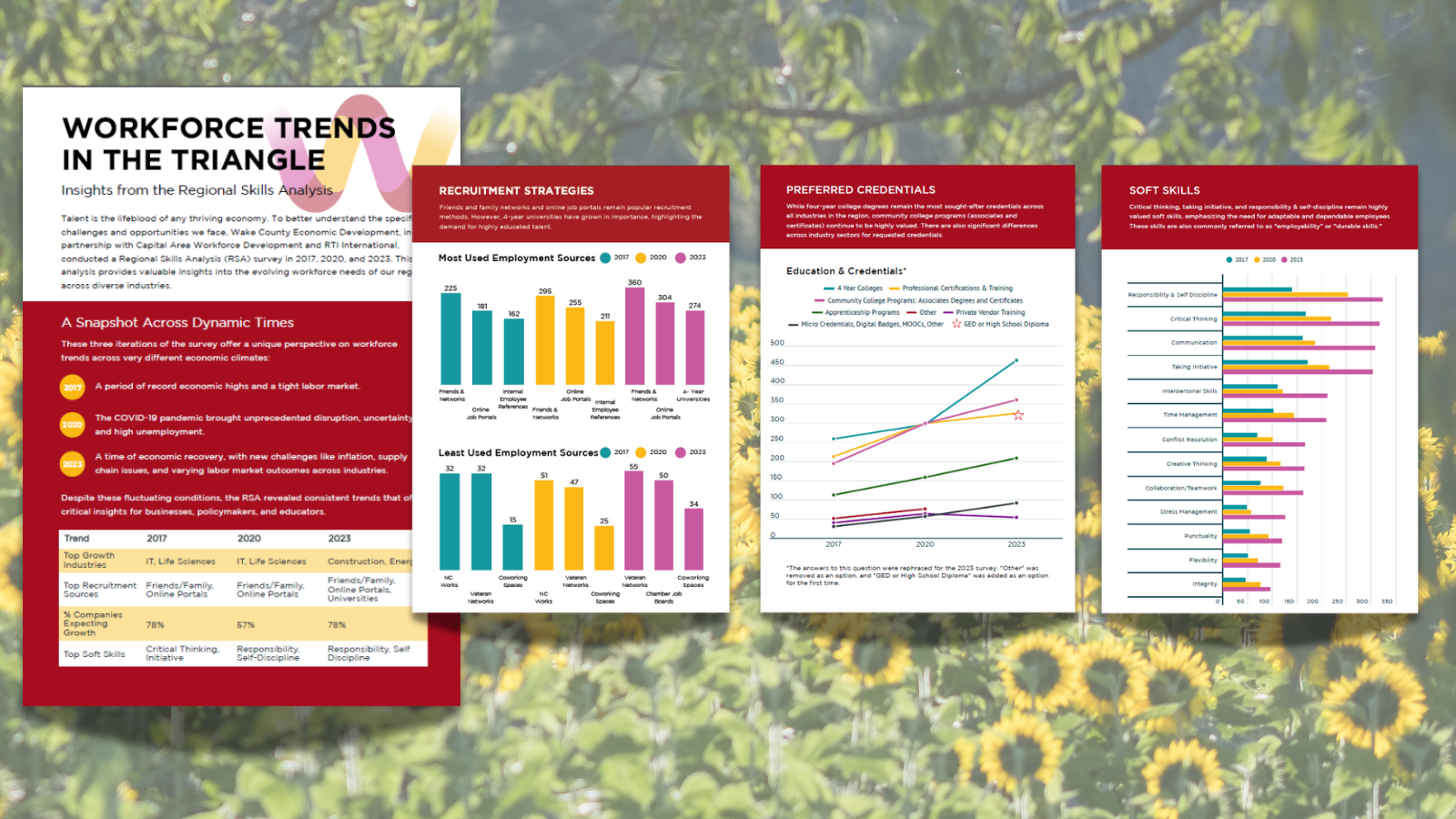
Talent is the lifeblood of any thriving economy. As discussed in the previous post, the Research Triangle faces a looming demographic drought that threatens our region's greatest asset: our skilled workforce. To better understand the specific challenges and opportunities we face, Wake County Economic Development, in partnership with Capital Area Workforce Development and RTI International, conducted a Regional Skills Analysis (RSA) survey in 2017, 2020, and 2023. This analysis provides valuable insights into the evolving workforce needs of our region across diverse industries.
Click here to download the report.
A Snapshot Across Dynamic Times
These three iterations of the survey offer a unique perspective on workforce trends across very different economic climates:
- 2017: A period of record economic highs and a tight labor market.
- 2020: The COVID-19 pandemic brought unprecedented disruption, uncertainty, and high unemployment.
- 2023: A period of economic recovery, with new challenges like inflation, supply chain issues, and varying labor market outcomes across industries.
Despite these fluctuating conditions, the RSA revealed consistent trends that offer critical insights for businesses, policymakers, and educators.
|
Overall Trends |
|||
|
Trend |
2017 |
2020 |
2023 |
|
Top Growth Industries |
IT, Life Sciences |
IT, Life Sciences |
Construction, Energy |
|
Top Recruitment Sources |
Friends/Family, Online Portals |
Friends/Family, Online Portals |
Friends/Family, Online Portals, Universities |
|
% Companies Expecting Growth |
78% |
57% |
78% |
|
Top Soft Skills |
Critical Thinking, Initiative |
Responsibility, Self-Discipline |
Responsibility, Self-Discipline |
- Shifting Industry Growth: While IT and Life Sciences dominated growth expectations in 2017 and 2020, Construction & Skilled Trades, and Energy, Utilities & Cleantech emerged as the top growth sectors in 2023. This reflects the region's focus on infrastructure development and sustainability amidst rapid growth.
- Consistent Recruitment Strategies: Friends and family networks and online job portals remain popular recruitment methods. However, 4-year universities have grown in importance, highlighting the demand for highly-educated talent.
- Fluctuating Growth Expectations: The percentage of companies expecting to grow dipped significantly in 2020 due to the pandemic but rebounded in 2023 signaling renewed optimism.
- Essential Soft Skills: Critical thinking, taking initiative, and responsibility & self-discipline remain highly valued soft skills, emphasizing the need for adaptable and dependable employees.
Industry-Specific Insights
|
Industry-Specific Insights |
|||||
|
Industry |
Top Soft Skill Challenge |
Valued Credentials |
Top Job Openings |
Key Hiring Skills |
% Companies Expecting Growth |
|
Healthcare & Social Assistance |
Critical Thinking |
4-Year Degrees (fluctuating) |
Nurses (increasing demand) |
Effective Communication |
79% (2017) - 87% (2023) |
|
Construction & Skilled Trades |
Communication (2023) |
Apprenticeships (shifting to 4-Year Degrees) |
Supervisors, Specialized Trades (fluctuating) |
Communication, Efficient Completion of Tasks |
67% (2017) - 87% (2023) |
|
Professional & Technical Services |
Responsibility/Self-Discipline |
4-Year Degrees |
Admin Assistants, Marketing, Accountants |
Ability to Work Efficiently |
55% (2020) - 79% (2023) |
|
Logistics, Transportation & Warehousing |
Critical Thinking (2023) |
Shifting (GED/HS to 4-Year/Community College) |
Technical roles (Mechanics increasing) |
Communication, Information Gathering & Analysis |
50% (2017) - 79% (2023) |
|
IT, Software & Analytics |
Critical Thinking |
4-Year Degrees, Certifications |
Software Developers, Cybersecurity (increasing) |
Communication, Remaining Current on Technology |
87% (2017) - 77% (2023) |
|
Restaurants, Lodging & Hospitality |
Responsibility/Self-Discipline |
4-Year Degrees (increasing) |
Food Prep, Supervisors (increasing) |
Customer Service, Food Safety, Communication |
46% (2020) - 76% (2023) |
|
Public Sector & Education |
Communication (2023) |
4-Year Degrees, Community College (increasing) |
Admin/Support, Facilities/Maintenance (increasing) |
Organization, Planning, Leadership (fluctuating) |
43% (2020) - 76% (2023) |
|
Life Science & Biosciences |
Critical Thinking |
4-Year Degrees, broader acceptance (2023) |
Quality Assurance, Engineers, Researchers (increasing) |
Technical Expertise, Project Management (increasing) |
88% (2020) - 75% (2023) |
|
Energy, Utilities & Cleantech |
Communication (2023) |
4-Year Degrees (increasing) |
Engineers, Technicians, Specialists (increasing) |
Project Management, Communication, Regulatory Compliance |
43% (2020) - 87% (2023) |
|
Manufacturing |
Responsibility/Self-Discipline |
GED/HS Diploma (increasing) |
Production Workers, Machine Operators, Engineers |
Communication, Resource Use, Tool Use |
81% (2017) - 67% (2023) |
Future Trends: Navigating the Demographic Drought
Looking ahead, the RSA data paints a vivid picture of the forces shaping the future of work in the Triangle. We're entering an era where technical and specialized skills will be paramount. This means a continued shift towards technical education and industry-specific credentials, though the value of a four-year degree certainly won't disappear. In fact, lifelong learning will be more critical than ever. Technology is transforming every industry at a breakneck pace, demanding continuous upskilling and reskilling to keep up with new processes and tools.
The workplace itself is also undergoing a transformation. Hybrid work models are here to stay, requiring workers to master the art of digital communication and self-management. But while flexibility is key, the value of in-person collaboration hasn't diminished. Striking a balance between remote work and face-to-face interaction for mentorship and team building will be essential.
And speaking of technology, get ready for the automation revolution! As routine tasks become increasingly automated, the demand for higher cognitive skills will soar. We can also expect to see entirely new job categories emerge focused on AI, machine learning, and data analysis.
But amidst all this technological advancement, human skills will remain invaluable. Critical thinking, adaptability, empathy, and communication will be highly prized. Companies will also prioritize employee well-being, recognizing the growing importance of mental health support and work-life balance.
The changing demographics of our workforce will also bring new challenges and opportunities. As Baby Boomers retire, we'll need to implement knowledge transfer strategies to bridge potential workforce gaps. This also presents a chance to create meaningful opportunities for older workers to remain engaged and contribute their valuable experience.
Sustainability will be another defining trend. The demand for green jobs in renewable energy, cleantech, and sustainable practices will surge. Companies across all sectors will integrate sustainability into their core operations, recognizing its importance for both the planet and their bottom line.
Finally, the very nature of work is evolving. The gig economy is expanding, requiring businesses to adapt to managing a blended workforce of employees and freelancers.
This is a future filled with both challenges and exciting possibilities. By understanding these trends and proactively preparing for them, the Triangle can ensure its workforce remains resilient, adaptable, and ready to thrive in the years to come.
Local Institutions: Building a Bridge to the Future
The challenges presented by the demographic drought and the evolving needs of our workforce require a collaborative response. Fortunately, here in the Triangle, we have institutions actively working to bridge the gap.
Wake Tech Community College is a key player, offering a diverse range of programs tailored to the needs of local industries. Their Customized Training Programs allow businesses to upskill their workforce in a way that directly addresses specific skill gaps. And with a strong focus on healthcare, Wake Tech is helping to meet the critical demand for skilled healthcare professionals, a need that will only intensify as our population ages. Furthermore, programs like “Propel” increase access to training by providing financial assistance, ensuring a more inclusive and diverse talent pool.
NC State University also plays a crucial role. Their commitment to expanding their engineering program is directly aligned with the RSA's findings, which highlight the growing need for engineers across various sectors. But their contribution goes beyond technical fields. With a broad range of programs in business, management, and the social sciences, NC State is equipping students with the well-rounded skills needed to navigate the complexities of the modern workplace.
Capital Area Workforce Development acts as a vital connector, bringing together job seekers, employers, and training providers. The Raleigh Pathways Center provides valuable workforce development training for young adults, preparing them for successful careers. Their Business Services help companies recruit, train, and retain talent, while NCWorks Career Centers offer essential resources and guidance to individuals navigating the job market.
These institutions are not just responding to current needs; they are anticipating future trends. They are actively collaborating with businesses and industry organizations to ensure their programs remain relevant and address emerging fields like clean energy and advanced manufacturing. And with a focus on lifelong learning, they provide opportunities for individuals to continuously upskill and reskill, ensuring our workforce remains adaptable and competitive.
However, we found in the RSA that small and medium sized businesses are heavily underutilizing the abundance of resources that exist in our community. Individuals and businesses may find themselves needing a clearer pathway to connect with the right programs and support systems. This is a key takeaway for community leaders to work on a future where accessing the wealth of opportunities in the Triangle is as seamless as the innovation that defines our region.
In the face of the demographic drought, these organizations offer a beacon of hope. Their dedication to providing accessible, relevant education and training is building a bridge to the future, ensuring the Triangle's workforce remains a driving force for economic growth and prosperity.
Conclusion
The Regional Skills Analysis provides a valuable roadmap for understanding the evolving workforce needs of the Research Triangle. By proactively addressing these trends and collaborating across sectors, we can build a resilient and adaptable workforce that thrives amidst the challenges and opportunities of the future. As we navigate the demographic drought, a focus on skills development, innovation, and inclusivity will be essential to ensure the continued economic vitality of our region.
Comments
There are no comments yet.
Leave a Comment